Understanding Magnesium Deficiency: A Complete Guide to Symptoms and Causes
Magnesium deficiency occurs when the body fails to get sufficient magnesium from food needed for energy production, bone and tooth development, and muscular functioning. Fortunately, magnesium is quite common in your foods, occurring abundantly in many vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds and lentils, milk and yogurt, and lean protein sources.
Besides, many canned foods, including morning cereals, are enriched in this mineral. So, if you don't want to suffer from muscle cramps, asthma, and hypertension, be sure to include magnesium-rich foods in your diet. But before that, don't forget to learn about the symptoms of magnesium deficiency and related complications in detail here!
What Are The Causes Of Magnesium Deficiency?
Your initial assumption might be that a poor diet causes a magnesium deficiency, but this is rare. Rather, magnesium insufficiency typically arises from health conditions or medications that impair the body's ability to use the mineral. The most common causes of magnesium insufficiency have been mentioned below:
- Diet and Age
- Diabetes
- Kidney diseases
- Gastrointestinal disease or Diarrhea
- Hypercalcemia
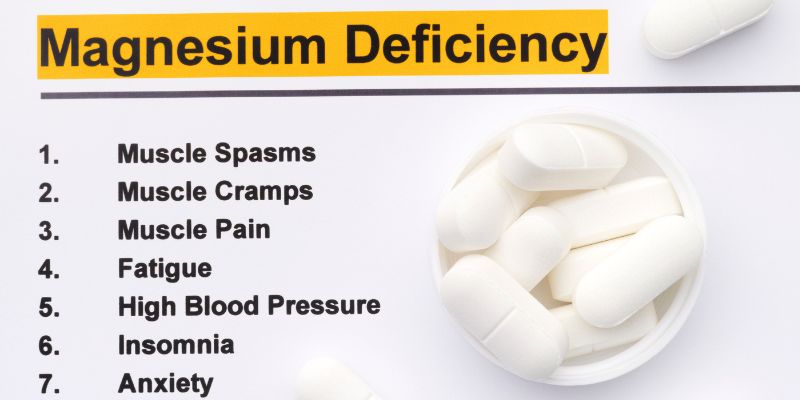
What Are The Symptoms Of Magnesium Deficiency?
Understanding the symptoms of magnesium deficiency is crucial for appropriate treatment. Low magnesium symptoms are typically minor at first and might be mistaken for other common diseases like nausea, vomiting, reduced appetite, weariness, and depression. An extreme magnesium deficiency in your body can raise the risk of:
Muscle Twitches And Cramps
Muscle cramps or twitches are one of the most prevalent symptoms of magnesium deficiency. Magnesium insufficiency can occasionally result in seizures or tremors. These symptoms could be triggered by an increase in the flow of calcium into neurons, which overexcites or hyperstimulates muscle cells. Unluckily, research indicates that magnesium pills do not assist in repairing this negative effect. Individuals will need to boost their magnesium levels through nutrition. If you get muscle spasms and aches frequently, see your doctor. Muscle twitches can be an undesirable outcome of certain medicines or a sign of neurological disorders like muscular dystrophy, multiple sclerosis, and myasthenia gravis.
Mental health Conditions
Insufficient magnesium levels have also been linked to mental disorders. A study was conducted in 2023 and found a link between magnesium supplementation and relieved depression. Mild anxiety has also been linked to magnesium deficiency, so this is something to consider if you've observed yourself experiencing more stress than normal. Magnesium insufficiency can also lead to a variety of mental health disorders, such as apathy, characterized by a lack of emotion. Furthermore, magnesium deficiency can have an undesirable effect on sleep. Magnesium supports the circadian rhythm. Therefore, inadequate amounts may result in poor sleep quality and insomnia. Magnesium increases calmness and reduces stress, which improves the quality of sleep. Several studies have found that taking magnesium pills can aid with insomnia.
Fatigue And Muscle Weakness
Magnesium deficiency symptoms include fatigue as well as muscular weakness. Insufficient magnesium levels may damage muscle activity and energy creation, resulting in sensations of stress and weakness in the body. Magnesium helps muscles to relax and contract, but how? Magnesium promotes ease in muscles by managing the quantity of calcium within muscle cells. When magnesium levels are low, muscles cannot properly calm down, resulting in stiffness and discomfort. Magnesium is also needed for adequate nerve communication, which is required for muscular contraction. Magnesium deficiency may interfere with this communication, weakening muscles. Those experiencing these symptoms may find routine tasks challenging.
Osteoporosis
Magnesium is a dietary nutrient required for bone formation and calcification, and its deficiency can increase the chance of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a complex illness that causes major changes in bone structure and reduction in bone mass. Magnesium deficiency can damage bones directly, yet it also reduces blood calcium levels, which are the primary constituents of bones. Other indications for osteoporosis include aging, insufficient physical activity, and inadequate vitamin D and K consumption, while magnesium itself cannot prevent the condition. That’s because magnesium is a cofactor, and the condition is linked to other nutrients, particularly calcium and vitamin D (both need to strengthen your bones and make them healthy).
High blood pressure
Magnesium deficiency can lead to hypertension, which increases the possibility of cardiac arrest, stroke, and renal damage. If you suffer from high blood pressure, try to get enough magnesium through diet instead of having supplements or consuming extra magnesium. For that, make magnesium-rich foods a part of your meals. Also, these foods can provide you with various nutrients (particularly fiber). The other advantage is that these foods contain a little salt, as excessive salt can cause hypertension.
Irregular Heartbeat
Magnesium is an electrolyte that maintains the heart's rhythm and electrical functions. When magnesium concentrations are low, the heart's electrical system becomes unsteady, resulting in a rapid pulse. Heart arrhythmia is another name for an irregular heartbeat. Arrhythmia can be difficult to detect because the symptoms are usually modest. It may induce difficulty breathing, chest discomfort, dizziness, and fainting. However, certain individuals develop cardiac palpitations (breaks between heartbeats) as an effect of their rhythmic heartbeats. A magnesium deficit might result in a shortage of potassium, which can cause irregular pulses.
Asthma
Magnesium deficiency and asthma can be linked. Researchers have discovered that low magnesium levels appear mostly in asthmatic patients rather than in healthy individuals. That’s because magnesium insufficiency induces calcium to block the respiratory tract, making breathing difficult. Oral magnesium consumption may be an effective cure for persistent asthma. Magnesium's anti-inflammatory and airway-relaxing effects could cause it. However, research on the positive effects of oral magnesium supplementation is inconclusive.
Conclusion:
Many individuals fail to obtain sufficient magnesium from their diet. It is rare for persons without a serious medical condition to suffer low magnesium or magnesium deficiency symptoms. Magnesium deficiency symptoms are usually modest until your levels drop significantly. Magnesium supplements address certain symptoms of magnesium insufficiency, but not all of them. In some circumstances, dietary adjustments are important to fulfill this deficiency. Identifying and treating magnesium deficiency is critical for sustaining overall wellness. People may combat magnesium insufficiency and enhance their general health by knowing the causes and symptoms. Anyone having deficient symptoms should consult a doctor for proper assessment and therapy.












